Ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilized egg implants outside of the womb, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. An ectopic pregnancy may not be noticeable and is only detected during routine pregnancy testing. Usually it will discovered by the 8th week of pregnancy. Most often, ectopic pregnancy happens within the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms
The symptoms of ectopic pregnancy are light vaginal bleeding, nausea and vomiting, abdominal cramps, dizziness, and heavy bleeding. Women that just had an ectopic pregnancy should wait for at least two full menstrual cycles before trying for another pregnancy. The reason for this to allow time for the fallopian tubes to recover.
ectopic pregnancy, image : www.ectopicpregnancyfoundation.org
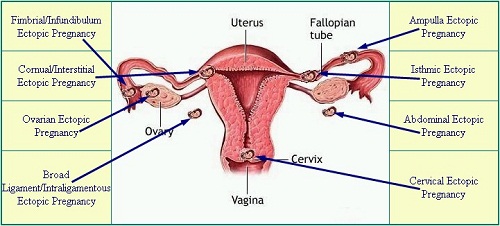
In normal pregnancies the fertilized egg enters the uterus and secretes itself in the lining of the uterus where it begins it’s process of division and growth. In about 1 in 100 pregnancies, however, the egg fails to implant within the womb. In 98% of these cases, the egg implants itself and begins developing within one of the fallopian tubes. As it begins dividing, the embryo embeds itself into the lining of the fallopian tube. This may result in restriction of blood vessels and resultant bleeding. An ectopic pregnancy is life threatening for the mother and will require an emergency procedure. There is a high likelihood the embryo will not survive.
The causes of an ectopic pregnancy are largely unclear. A damaged fallopian tube that prevents the fertilized egg from entering the uterus forcing it to implant itself in the fallopian tube is an obvious problem. Researchers have identified that a higher risk of an ectopic pregnancy exits if women use an intrauterine device (IUD) as a form of birth control, have had a sexually transmitted disease (STD), have a congenital deformity of the fallopian tube and suffer from pelvic scarring or Ashermans Disease. The use of fertility drugs and infertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) have also been recognized as potential contributors to an ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatments
Treatment for an ectopic pregnancy can be classified as either medical or surgical. Medical treatment involves the use of an ant folate drug called methotrexate. This drug will have the effect of terminating the life of the growing embryo. The embryo may then be expelled as an abortion or reabsorbed by the body. Surgical treatment is usually undertaken if hemorrhaging has already occurred. Patients may also opt for surgical treatment in an attempt to save the embryo. The surgeon will gain pelvic access by means of small incisions in the abdomen or pelvis. Once access is obtained the surgeon will either remove just the embryo or the entire fallopian tube.
Successful insertion of the extracted fetus into the womb is extremely rare. There have been two documented cases where this has taken place, resulting in live births. The danger to the life of the mother is heightened during this procedure. When a reinsertion is not attempted. However, the recovery rate for women is very good. The death rate in the Western world is 1 death in every 3,210 women who undergo an ectopic pregnancy procedure.
Related external post for you at Medicinenet here.
More posts from Babywoop.com :
– What is Ovarian Cyst?



 Saving...
Saving...