The ovary is a gland wherein the egg cells or ova are produced. Under the effect of the luteinizing hormone and the gonadotropic hormone, an ovarian follicle expels a single mature egg. The ovary however can normally have a number of hidden cysts throughout a woman’s lifetime.
ovarian cyst, image : myhealth.alberta.ca
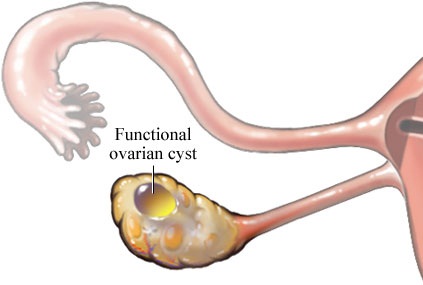
Ovarian cysts are closed, sac-like structures within the ovary that are filled with a liquid or semisolid substance. They are fairly common. Ovarian cysts can form for a numerous reasons. Many women have ovarian cysts at some time during their lives. Most ovarian cysts have no pain and harmless, and will disappear without treatment within a few months as they often go undiagnosed. However, ovarian cysts that have ruptured can produce serious symptoms.
Symptoms which might include: pain in the lumbosacral area, bloating in the abdomen, dysmenorrhea, and abnormal bleeding. Some mild symptoms might include: sudden weight gain, nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite. If you experience these symptoms, it is best to report this to your physician for the appropriate laboratory work-ups. Your gynecologist usually diagnoses cysts initially by checking for lumps in your pelvic area. Ovarian cysts are usually noncancerous but if a number of lumps are detected, it might lead to ovarian cancer.
Usual tests would be ultrasound, CT scans and blood works which will check the level of hormones. This is because rising hormones like luteinizing hormone, estradiol, and testosterone may have an impact on the cyst also.
Ovarian cysts do not usually affect a woman’s ability to conceive. Usually, the cysts get dissolved on their own. Your obstetrician will not recommend any procedure but will suggest that you check yourself often. The doctor will advise a follow-up to observe for any malignancies regarding the cyst. Contraceptive pills are sometimes recommended to reduce the risk of the cyst being malignant. Birth control pills tend to lessen the risk the more you take them.
If the cyst is large and causes pain, it needs to be removed. Surgery may be the best option. It may be possible to carry out the procedure using laparoscopy, which may help preserve your fertility. It uses a very small incision so that an endoscope may be inserted. This surgery is typically used for early detected cysts which are small.
When a cyst is bigger, the procedure needed is called laparotomy. It would entail a more complicated surgery since it requires a bigger incision. Therefore, it has a longer post surgery healing time for the patient. Most likely, recovery time would be around six to eight weeks. There is always a chance that the surgeon might remove one of your right or left ovaries. If only one is removed, your fertility will be reduced by just a little. If both of them are removed, you might experience an early menopause. This would make you unable to bear children.
To avoid this costly procedure early prevention can be achieved through pelvic examination by your gynecologist. Plot your monthly menstrual cycle if they are regular and any pain near the hip area should be reported to your doctor.



 Saving...
Saving...
One Comment